3D Printing in Architecture
3D printing for the production of architectural models
Architectural models are small replicas of buildings or cities used by architects, engineers and designers to present their designs and visions. In the past, such models were made manually from wood, papier-mâché or plastic, which required time and effort. Nowadays, however, there is the possibility of producing architectural models with the help of 3D printers.
3D printers are machines that can additively produce three-dimensional objects from various materials using digital models. Additive manufacturing is particularly useful in architecture, as they allow complex shapes and details to be accurately reproduced. Architectural models made by 3D printing are thus not only faster and cheaper to produce, but often also more detailed and precise than traditional models.
To produce an architectural model using 3D printing, a digital model must first be created. This can be done with the help of special software such as AutoCAD or SketchUp. Once the digital model is complete, it is transferred to the 3D printer, which then builds the model from the desired material.
If the plans of a building change, architects can use 3D printing to quickly create a modified model without having to start the entire model from scratch. All that needs to be done is to adjust the 3D file and put the new model into print. This allows them to react quickly to changes and make the best decisions for the building and their client.
Another advantage of 3D printing in architecture is the ability to produce models in different sizes and shapes. While traditional architectural models are often only available in a limited number of sizes, 3D printers can print models in almost any size. The ability to print models in different colours and materials also opens up new creative possibilities for architects and designers.
The use of 3D printing has revolutionised the way architects work, allowing them to work faster and more precisely. Thanks to additive manufacturing, they can present their ideas better and make decisions faster, making their projects more effective and sustainable.
Your advantages at a glance
- Fast and precise production of architectural models
- Possibility to make changes to the model quickly and easily
- Great design freedom
- Different scale levels can be produced, even in one production step
- Several (non-contiguous buildings) can be produced in one construction job
- Expansion of material options through the use of plastics and metals that would not be possible to process manually
Which materials are suitable for architectural models?
There are various materials that can be used for 3D printing architectural models, including plastics, metals, ceramics and even glass. However, the most commonly used materials are plastics such as PA11 and PA12. These are lightweight, relatively inexpensive and strong, making them particularly suitable for printing prototypes and concept models.
There are also a number of metals that can be used for 3D printing architectural models, such as aluminium or stainless steel. However, additively manufactured models made of metal are significantly more expensive than those made of plastic, which is why they are only suitable for simple concept models to a limited extent, but rather for special exhibition pieces or art objects.
Which material is best suited for the architectural model depends on the requirements of the model, its purpose and the architect's preferences.
Types of 3D printed architectural models
A 3D printed architectural model can look and be constructed in many different ways, depending on its purpose and level of detail. Here are some of the most common types:
Concept models: These architectural models are used to represent the basic idea or concept of a design. They are often abstract and less detailed.
Working models: These models are created during the design process to test and develop different design ideas. They are often flexible and can be easily adapted.
Presentation models: These architectural models are more detailed and are used to present the final design-in to an audience. They are often aesthetically pleasing and show materials, colors and textures.
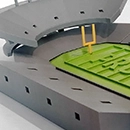
Urban models: These models show larger urban contexts and often include multiple buildings and infrastructures. They are used to illustrate urban planning and development.
Functional models: These architectural models show specific functional aspects of a building, such as the structure, ventilation or lighting. They are often technical and detailed.
Post-processing 3D printed architectural models
Post-processing 3D printed architectural models is an important step to improve the quality and appearance of the model. Here are some of the most common post-processing steps:
Sanding: Smoothing the surface with sandpaper in different grits (e.g. 120, 220, 400, 800, 1000). This helps to remove visible layers and irregularities, especially on rough surfaces such as those from selective laser sintering.
Filling and filling: Using filler or putty to smooth out imperfections. This is often applied and smoothed with a spatula.
Varnishing and painting: Applying layers of paint with spray paint or brushes to achieve the desired look. Special effects, details and textures can also be added here.
Special techniques: These include, for example, vapor smoothing (chemical smoothing) and other methods to further enhance the surface.
These steps help to make the 3D-printed architectural model look professional and appealing.
Future trends in 3D printing for architecture
The architecture industry is undergoing a real transformation thanks to 3D printing. While 3D-printed architectural models are already finding their way into the standards of the design and presentation phase, development is already going far beyond this.
One particularly exciting trend is the use of sustainable materials such as recyclable plastics or ecological concrete mixtures, which not only conserve resources but are also more climate-friendly. Hybrid models in which different materials are combined – for example transparent plastics for window surfaces or flexible elements for movable structures – also allow designs to be presented even more realistically.
In addition, the level of detail is constantly improving thanks to new printing technologies that enable finer structures and complex geometries.
The combination of 3D printing with augmented reality (AR) opens up another exciting possibility: digital architectural models can be combined with physical 3D-printed models via an app to enable interactive presentations. This allows architects to offer their clients an immersive experience and present design decisions even more vividly.
3D printing therefore remains one of the most innovative technologies for the world of architecture – and developments show that its potential is far from exhausted.
Future trends in 3D printing for architecture
The architecture industry is undergoing a real transformation thanks to 3D printing. While 3D-printed architectural models are already finding their way into the standards of the design and presentation phase, development is already going far beyond this.
One particularly exciting trend is the use of sustainable materials such as recyclable plastics or ecological concrete mixtures, which not only conserve resources but are also more climate-friendly. Hybrid models in which different materials are combined – for example transparent plastics for window surfaces or flexible elements for movable structures – also allow designs to be presented even more realistically.
In addition, the level of detail is constantly improving thanks to new printing technologies that enable finer structures and complex geometries.
The combination of 3D printing with augmented reality (AR) opens up another exciting possibility: digital architectural models can be combined with physical 3D-printed models via an app to enable interactive presentations. This allows architects to offer their clients an immersive experience and present design decisions even more vividly.
3D printing therefore remains one of the most innovative technologies for the world of architecture – and developments show that its potential is far from exhausted.
Note: AI-generated images are used on this page.



 Deutsch
Deutsch English
English Italiano
Italiano